Showing information for Pune. View Pune-specific page →
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) - Advanced Heart Surgery
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a surgical procedure that improves blood flow to the heart by creating new routes around narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. This procedure helps reduce chest pain and lowers the risk of heart attacks.
Minimally Invasive
Advanced techniques with minimal pain
Modern Technology
State-of-the-art equipment
Expert Doctors
Specialized in treatment
Quick Recovery
Return to normal activities fast
Also Known As:
Book an Appointment
What is Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)?
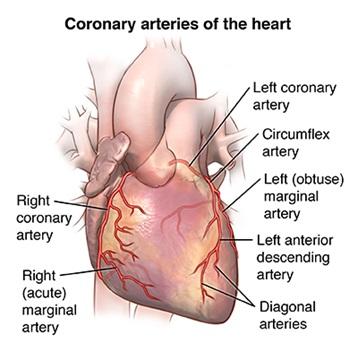
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a major surgical procedure used to treat coronary heart disease. During CABG surgery, a healthy blood vessel (graft) taken from the leg, arm, or chest is used to create a new pathway for blood to flow around a blocked coronary artery. This restores adequate blood flow to the heart muscle, improving heart function and reducing symptoms of coronary artery disease. CABG is one of the most common and effective treatments for severe coronary artery disease.
Trigger Foods to Avoid in a Diet
Saturated Fats
Can increase cholesterol levels and worsen arterial blockage
Trans Fats
Significantly increases risk of heart disease
High Sodium Foods
Raises blood pressure and strains the heart
Refined Sugars
Can lead to diabetes and increased cardiac risk
Processed Meats
High in sodium and unhealthy fats
Alcohol (Excess)
Can weaken heart muscle and raise blood pressure
Symptoms for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Chest Pain (Angina)
Pressure, squeezing, or burning sensation in the chest, especially during physical activity
Shortness of Breath
Difficulty breathing during exertion or at rest due to inadequate blood flow
Fatigue
Persistent tiredness and lack of energy, even with minimal activity
Heart Palpitations
Irregular heartbeat or awareness of heart beating
Weakness
Feeling weak or dizzy due to reduced blood flow to the body
Nausea or Indigestion
Digestive discomfort that may signal heart problems, especially in women
Common Causes of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Atherosclerosis
Buildup of fatty deposits (plaques) in the coronary arteries that narrow blood vessels
High Cholesterol
Elevated LDL cholesterol contributes to plaque formation in arteries
High Blood Pressure
Chronic hypertension damages artery walls and accelerates plaque buildup
Diabetes
High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and increase atherosclerosis risk
Smoking
Tobacco use damages artery linings and accelerates coronary artery disease
Family History
Genetic predisposition increases risk of coronary artery disease
Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Age Over 65
Risk increases significantly with advancing age
Male Gender
Men have higher risk, though risk increases for women after menopause
Obesity
Excess weight increases strain on the heart and cardiovascular system
Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity weakens the heart and circulatory system
Stress
Chronic stress can damage arteries and worsen heart disease
Poor Diet
Diet high in fats, cholesterol, and sodium accelerates disease progression
Indication of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Severe Coronary Artery Disease
Multiple blocked arteries requiring surgical intervention
Left Main Coronary Artery Disease
Critical blockage in the main artery supplying the left side of heart
Failed Angioplasty
When stenting or balloon angioplasty has not been successful
Triple Vessel Disease
Blockages in three or more major coronary arteries
Heart Attack with Complications
Acute myocardial infarction requiring immediate bypass
Unstable Angina
Chest pain at rest or with minimal exertion despite medication
Complications if Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) Left Untreated
Heart Attack
Complete blockage can cause myocardial infarction
Heart Failure
Weakened heart muscle unable to pump blood effectively
Arrhythmias
Irregular heart rhythms that can be life-threatening
Stroke
Reduced blood flow to the brain due to arterial disease
Sudden Cardiac Death
Unexpected cardiac arrest without warning
Cardiogenic Shock
Severe reduction in blood flow leading to organ failure
Diagnosis
Proper diagnosis involves comprehensive cardiac evaluation including detailed patient history, physical examination, and advanced diagnostic tests to assess the extent of coronary artery disease and determine if CABG surgery is the most appropriate treatment option.
Diagnostic Methods
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to assess heart rhythm and detect signs of heart attack
- Echocardiogram to evaluate heart structure and pumping function
- Coronary Angiography (gold standard) to visualize blocked arteries
- Stress Test to evaluate heart performance under physical exertion
- CT Angiography for non-invasive imaging of coronary arteries
- Blood tests including lipid profile, troponin, and cardiac enzymes
Surgical Treatment Options
Our advanced surgical procedures provide effective, long-term relief
Traditional CABG (On-Pump)
The most common approach where the heart is temporarily stopped and a heart-lung bypass machine maintains circulation while the surgeon grafts new blood vessels to bypass blocked arteries.
Recovery Time
6-12 weeks for full recovery
Anesthesia
General anesthesia
Off-Pump CABG (Beating Heart Surgery)
A technique where bypass surgery is performed on the beating heart without using a heart-lung machine. Special stabilizing devices hold the area of the heart being worked on steady.
Recovery Time
4-8 weeks for full recovery
Anesthesia
General anesthesia
Minimally Invasive CABG (MIDCAB)
A less invasive approach using smaller incisions between the ribs rather than opening the entire chest. Typically used for single-vessel disease of the left anterior descending artery.
Recovery Time
3-6 weeks for full recovery
Anesthesia
General anesthesia
Traditional CABG (On-Pump)
The most common approach where the heart is temporarily stopped and a heart-lung bypass machine maintains circulation while the surgeon grafts new blood vessels to bypass blocked arteries.
Recovery Time
6-12 weeks for full recovery
Anesthesia
General anesthesia
Off-Pump CABG (Beating Heart Surgery)
A technique where bypass surgery is performed on the beating heart without using a heart-lung machine. Special stabilizing devices hold the area of the heart being worked on steady.
Recovery Time
4-8 weeks for full recovery
Anesthesia
General anesthesia
Minimally Invasive CABG (MIDCAB)
A less invasive approach using smaller incisions between the ribs rather than opening the entire chest. Typically used for single-vessel disease of the left anterior descending artery.
Recovery Time
3-6 weeks for full recovery
Anesthesia
General anesthesia
Preventive Measures
Heart-Healthy Diet
Follow a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and omega-3 fatty acids while limiting saturated fats and sodium.
Regular Exercise
Engage in moderate aerobic activity for at least 150 minutes per week to strengthen the heart and improve circulation.
Quit Smoking
Eliminate tobacco use completely to reduce arterial damage and improve cardiovascular health.
Stress Management
Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to reduce cardiac strain.
Weight Management
Maintain a healthy BMI through balanced diet and regular physical activity to reduce heart workload.
Medication Adherence
Take prescribed medications including statins, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and antiplatelet drugs as directed.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) Types and Surgical Procedures
Single Vessel CABG
Description: Bypass surgery performed when only one coronary artery is significantly blocked, typically the left anterior descending (LAD) artery.
Surgical Procedure: Single graft placement, often using the left internal mammary artery (LIMA) to bypass the blocked segment.
Double Vessel CABG
Description: Surgical procedure when two major coronary arteries have significant blockages requiring bypass.
Surgical Procedure: Two grafts are placed to restore blood flow to affected areas of the heart muscle.
Triple Vessel CABG
Description: The most common type, performed when three major coronary arteries are blocked, affecting multiple areas of the heart.
Surgical Procedure: Three or more grafts using a combination of arterial and venous grafts to ensure complete revascularization.
Quadruple (Quad) Bypass
Description: Extensive surgery when four or more coronary arteries or their branches require bypass grafting.
Surgical Procedure: Multiple grafts (typically 4-5) are placed to address all significant blockages throughout the coronary system.
Redo CABG
Description: Repeat bypass surgery performed when previous grafts have failed or new blockages have developed in other arteries.
Surgical Procedure: Complex procedure requiring careful navigation around scar tissue from previous surgery while placing new grafts.
Emergency CABG
Description: Urgent bypass surgery performed during or immediately after a heart attack when the patient is unstable and angioplasty is not feasible.
Surgical Procedure: Rapid surgical intervention to restore blood flow and save heart muscle from permanent damage.
Why choose Total Surgicare for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) Surgery?
Expert Cardiac Surgeons
At Total Surgicare, our cardiac surgical team has extensive experience performing CABG procedures with high success rates. Our surgeons are trained in the latest techniques and stay updated with advances in cardiac surgery.
State-of-the-Art Cardiac Facility
We have advanced cardiac catheterization labs, modern operating theaters equipped with the latest technology, and dedicated cardiac ICU facilities to ensure the best outcomes for our patients.
Comprehensive Pre and Post-Operative Care
From initial consultation through complete recovery, we provide comprehensive cardiac care including cardiac rehabilitation programs, dietary counseling, and long-term follow-up to ensure optimal heart health.
Multidisciplinary Team Approach
Our cardiac care team includes cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, anesthesiologists, cardiac nurses, physiotherapists, and nutritionists who work together to provide holistic care tailored to each patient's needs.